This time we will disassemble an LED energy-saving lamp (bread light) to see how much the structure inside is different from ordinary energy-saving lamps.
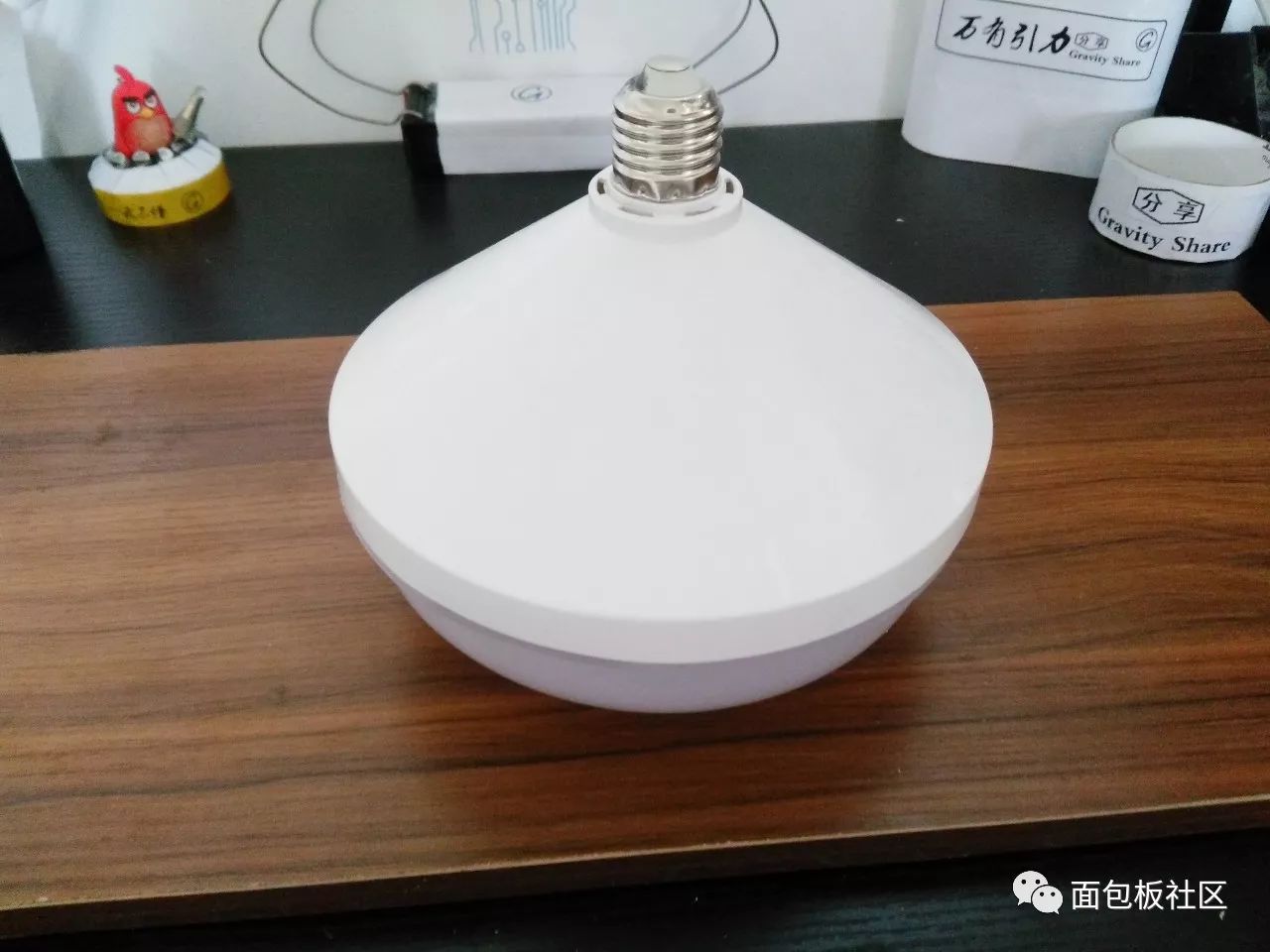

60W LED energy saving lamp (bread light)
First, the preparation for dismantling
Main tools & materials preparation 1, LED energy-saving lamps 1, 2 screwdrivers, electric soldering iron, etc.
Second, the process of disassembly
Firstly, the light-transmitting lamp cover of the LED is disassembled, and a large-area aluminum substrate can be seen, and an LED circuit control board is arranged thereon, and the power input is a screw port 220V lamp holder:
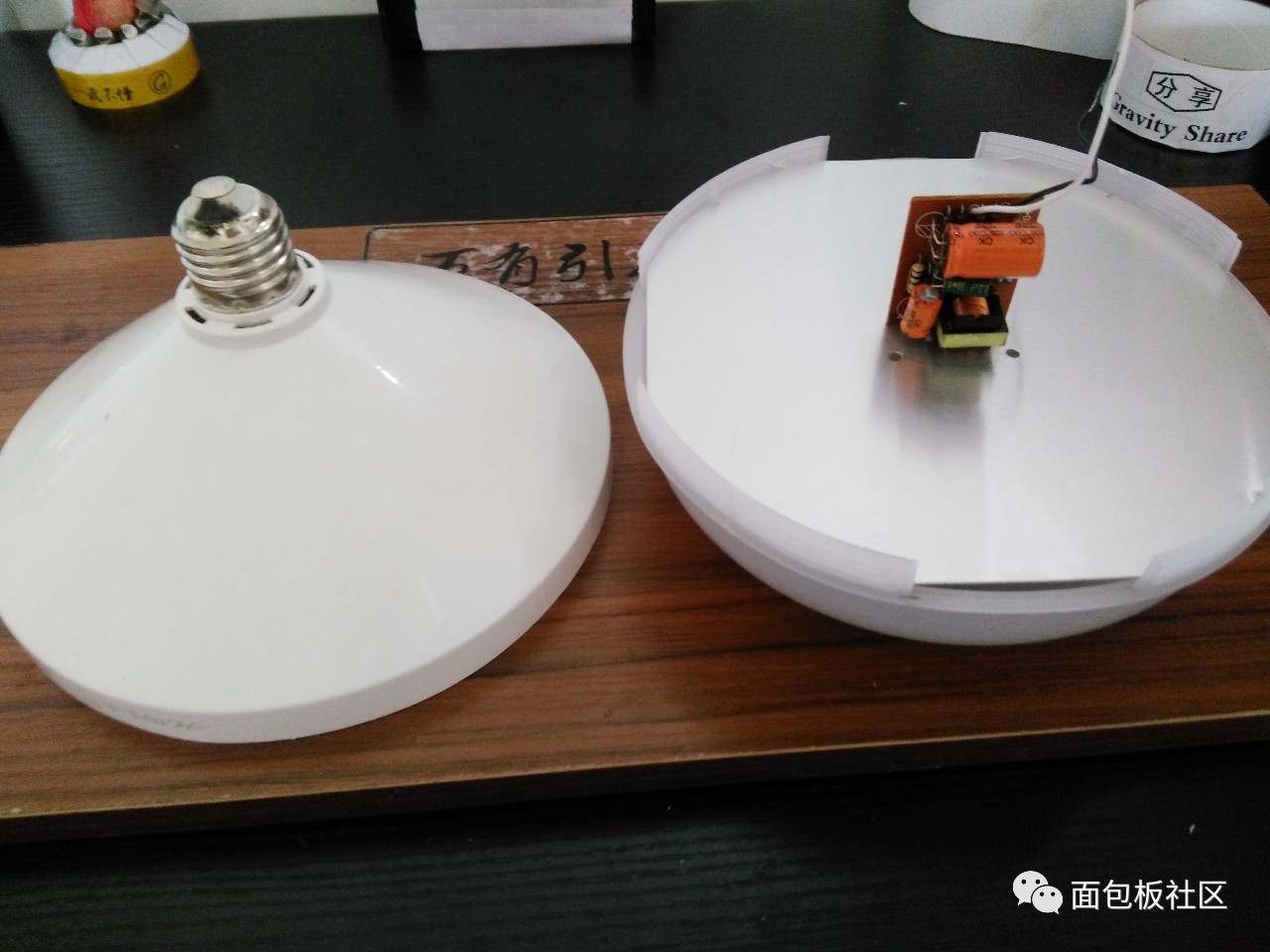

Unpacking the lampshade
LED light-emitting surface, 43 groups connected in series after 3 parallel connection, the above 3*43 group LED lamp beads are evenly arranged according to concentric circles:
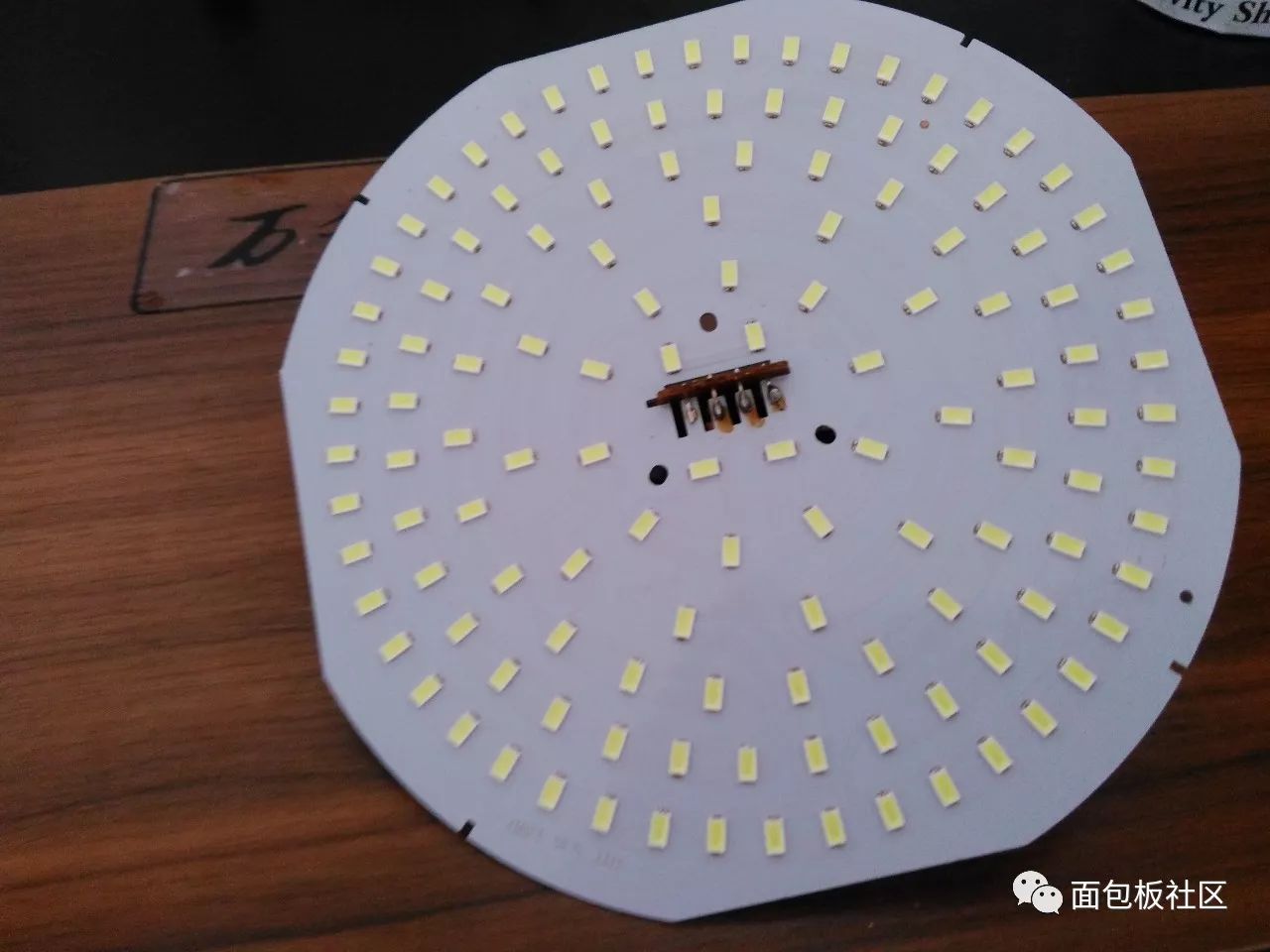
LED light board
The LED light board is welded to its control board, the middle two are positive and negative, and the other two are auxiliary fixed:
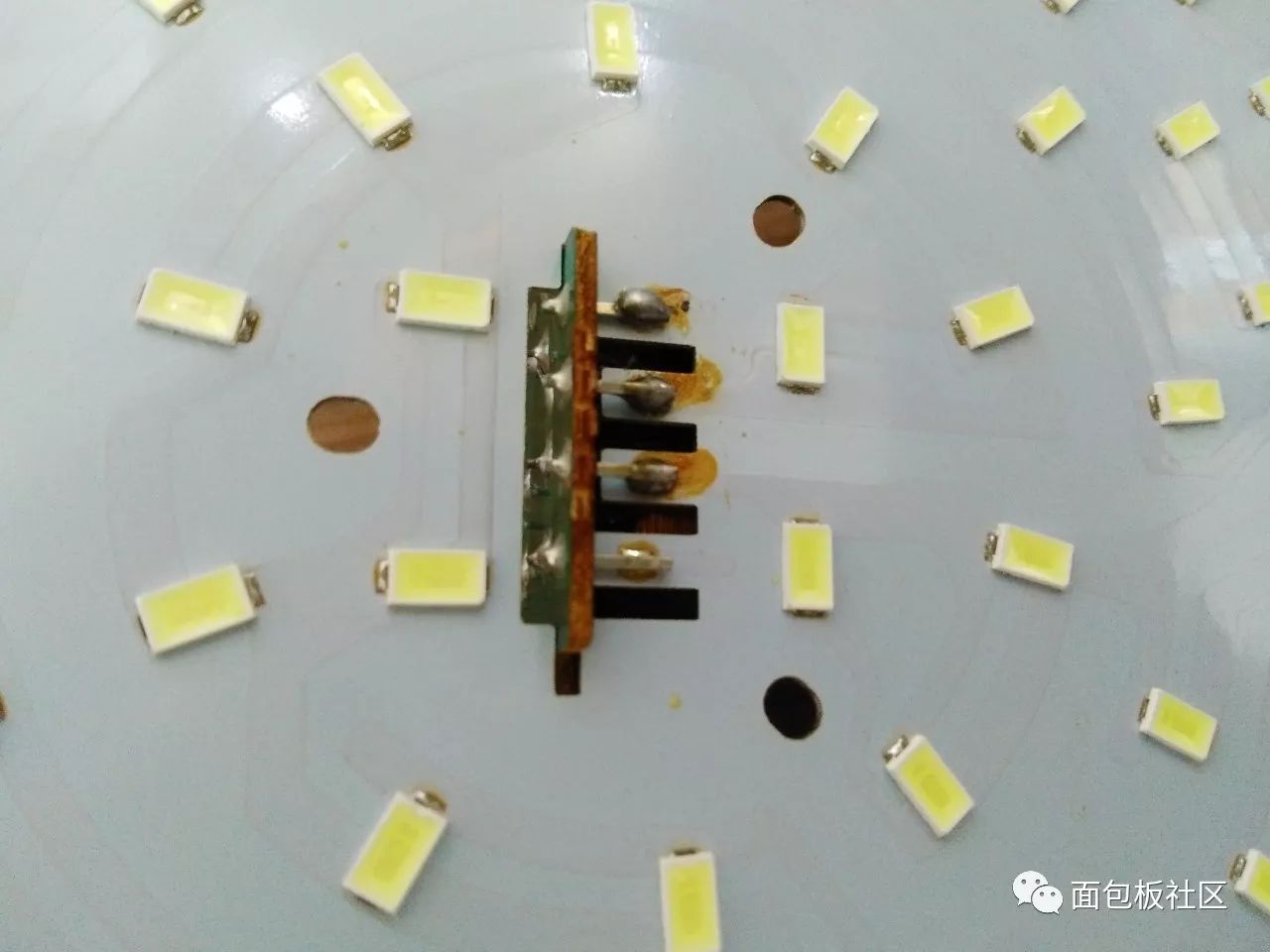

Junction
LED control panel:
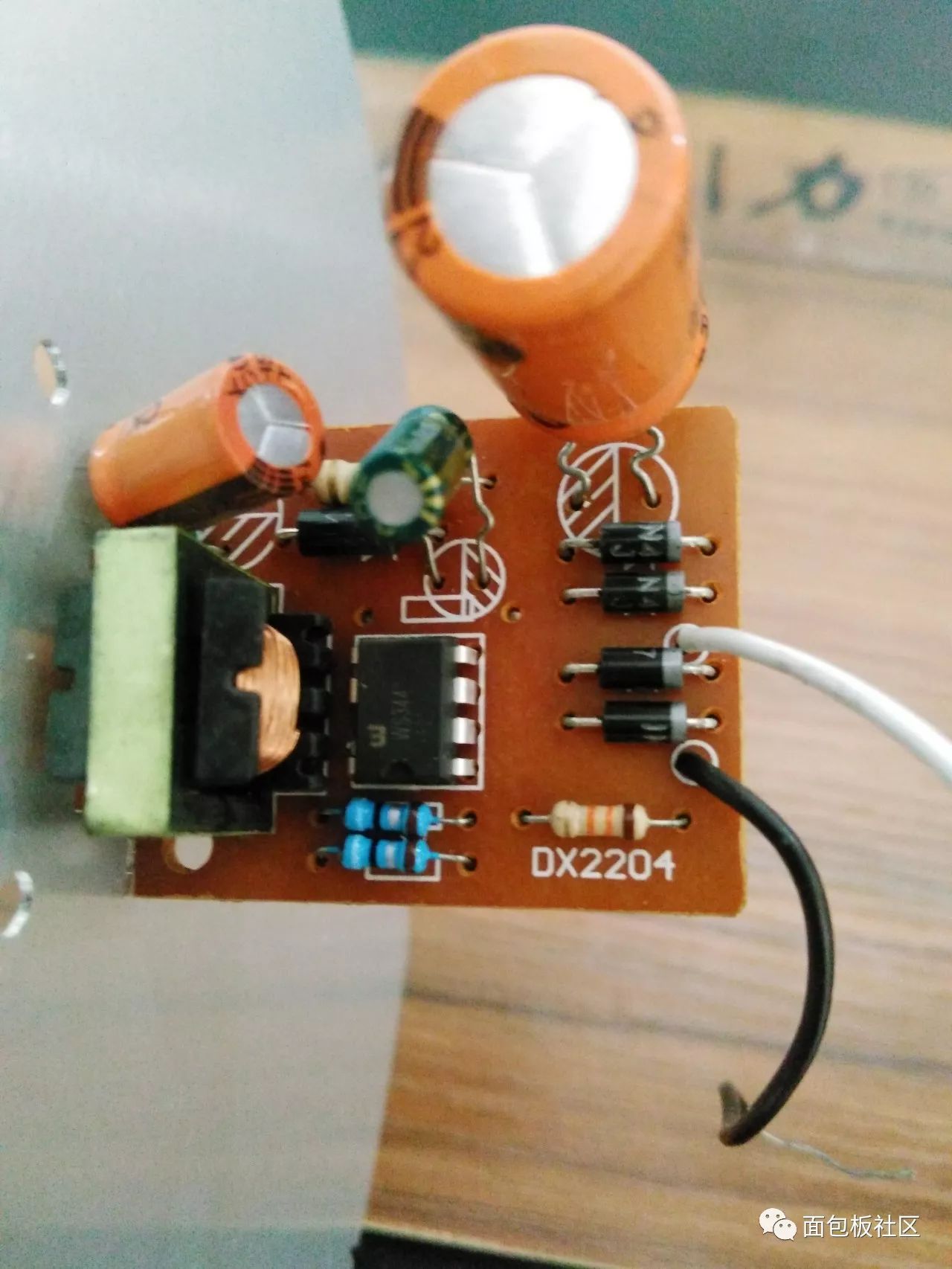

Control panel
The main control chip of the 7Pin pin:
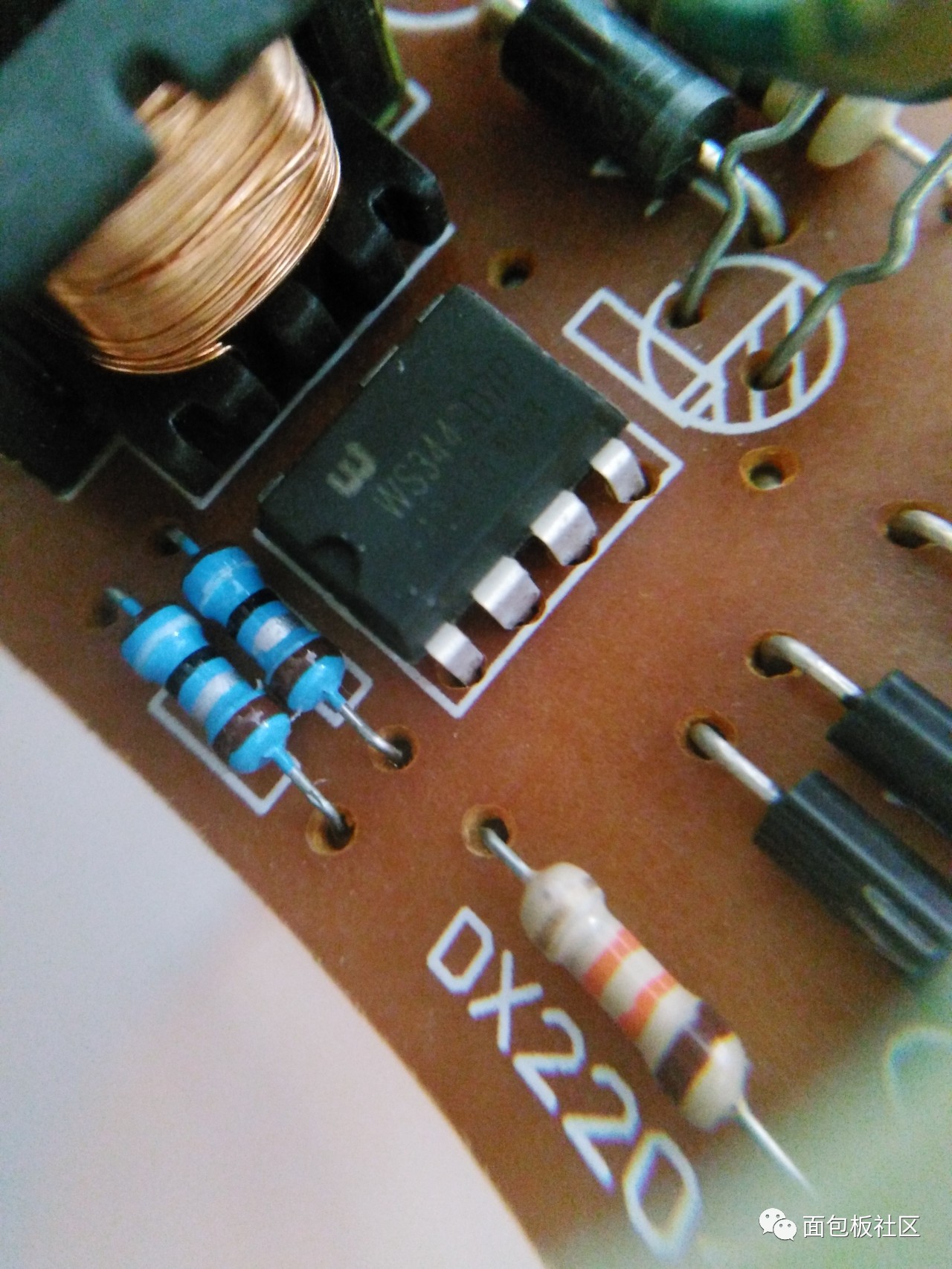
Control chip
A close look at the chip model is WS3442D7P: 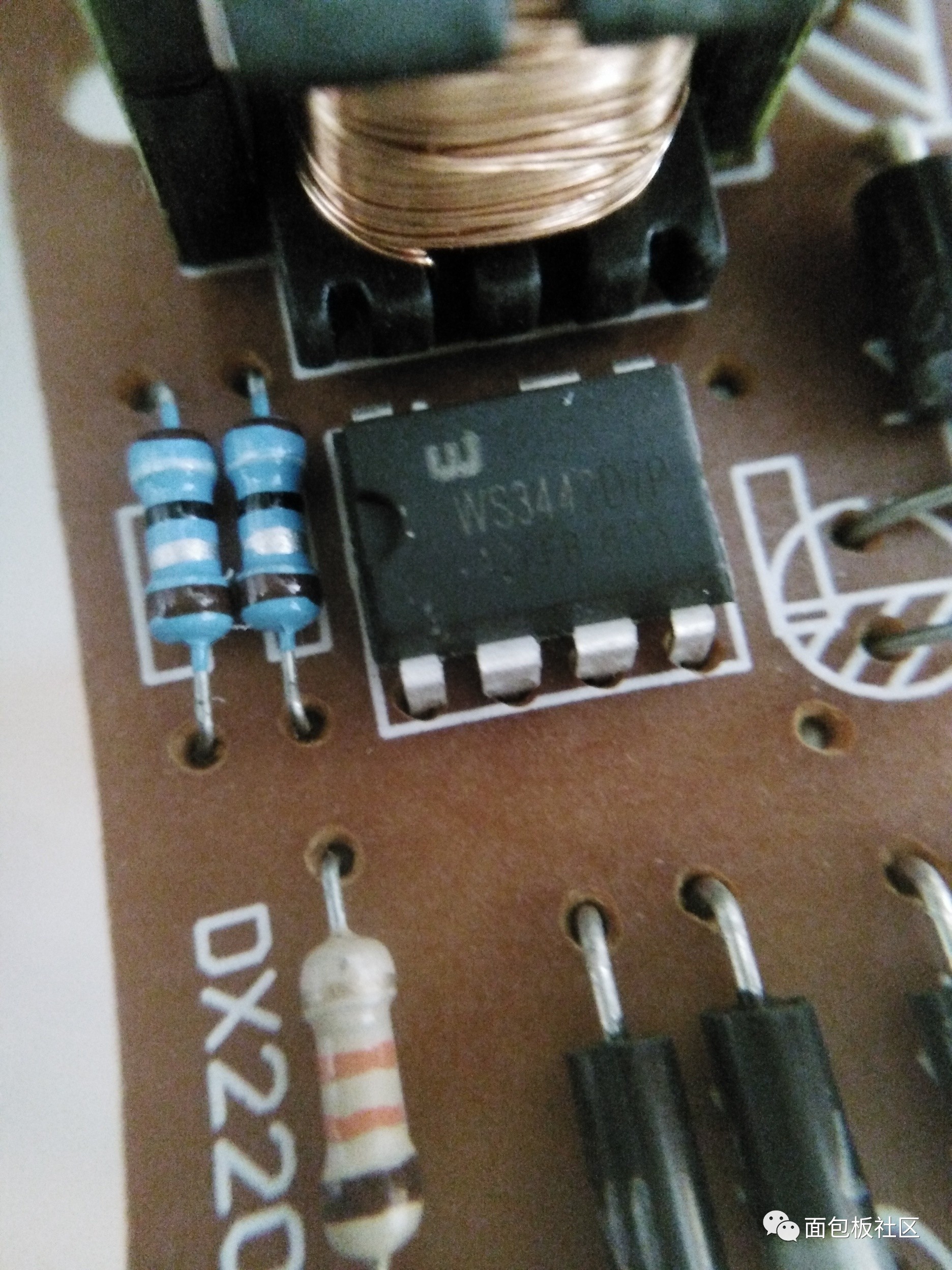 WS3442D7P
WS3442D7P
On the back of the LED control board, this PCB is a single-sided printed bakelite: 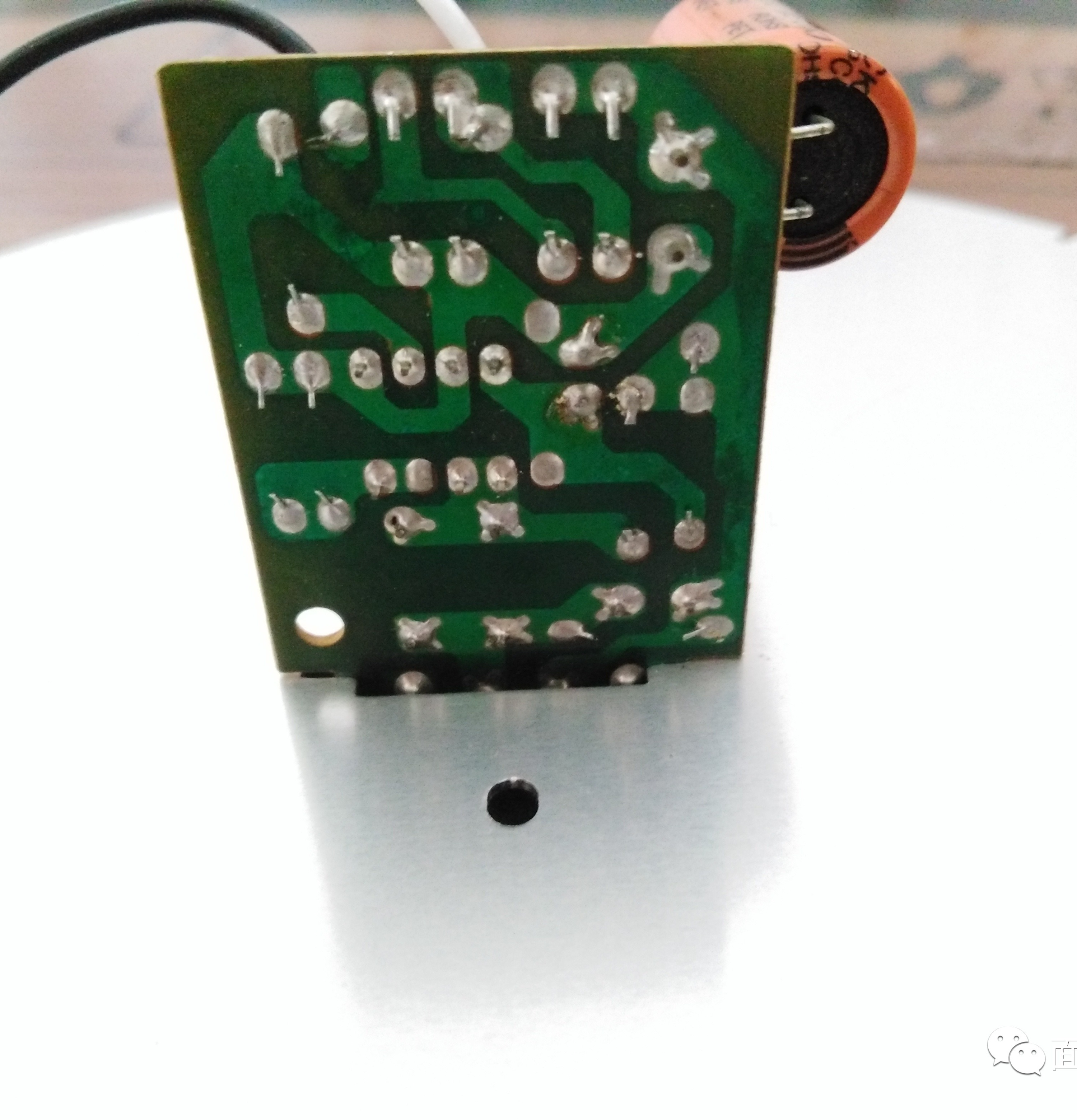 Back solder joint
Back solder joint
Use soldering iron to separate the control board from the solder joint of the aluminum substrate:
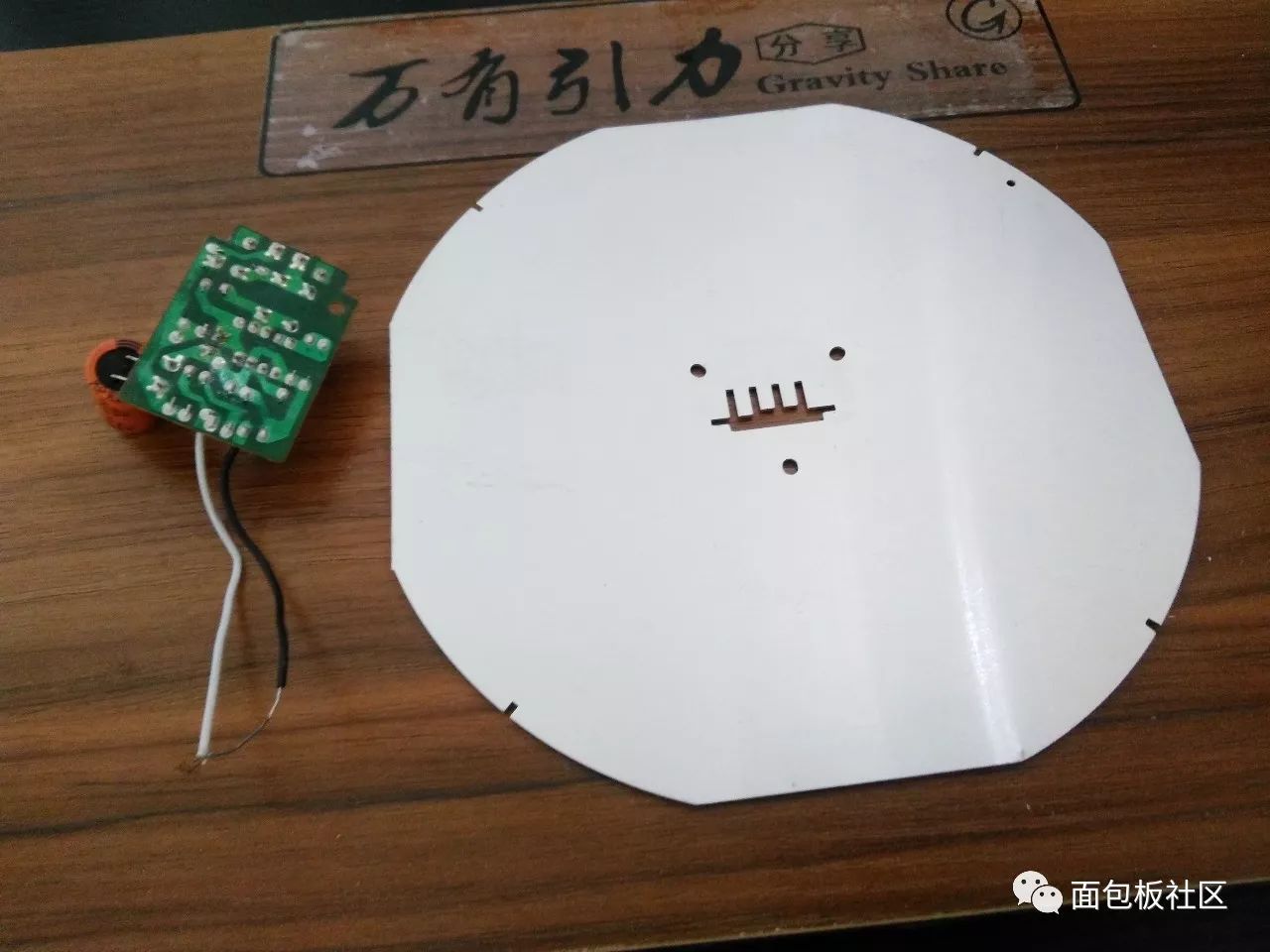

Remove the control panel
The four connection points on the control board are connected using straight pin welding:
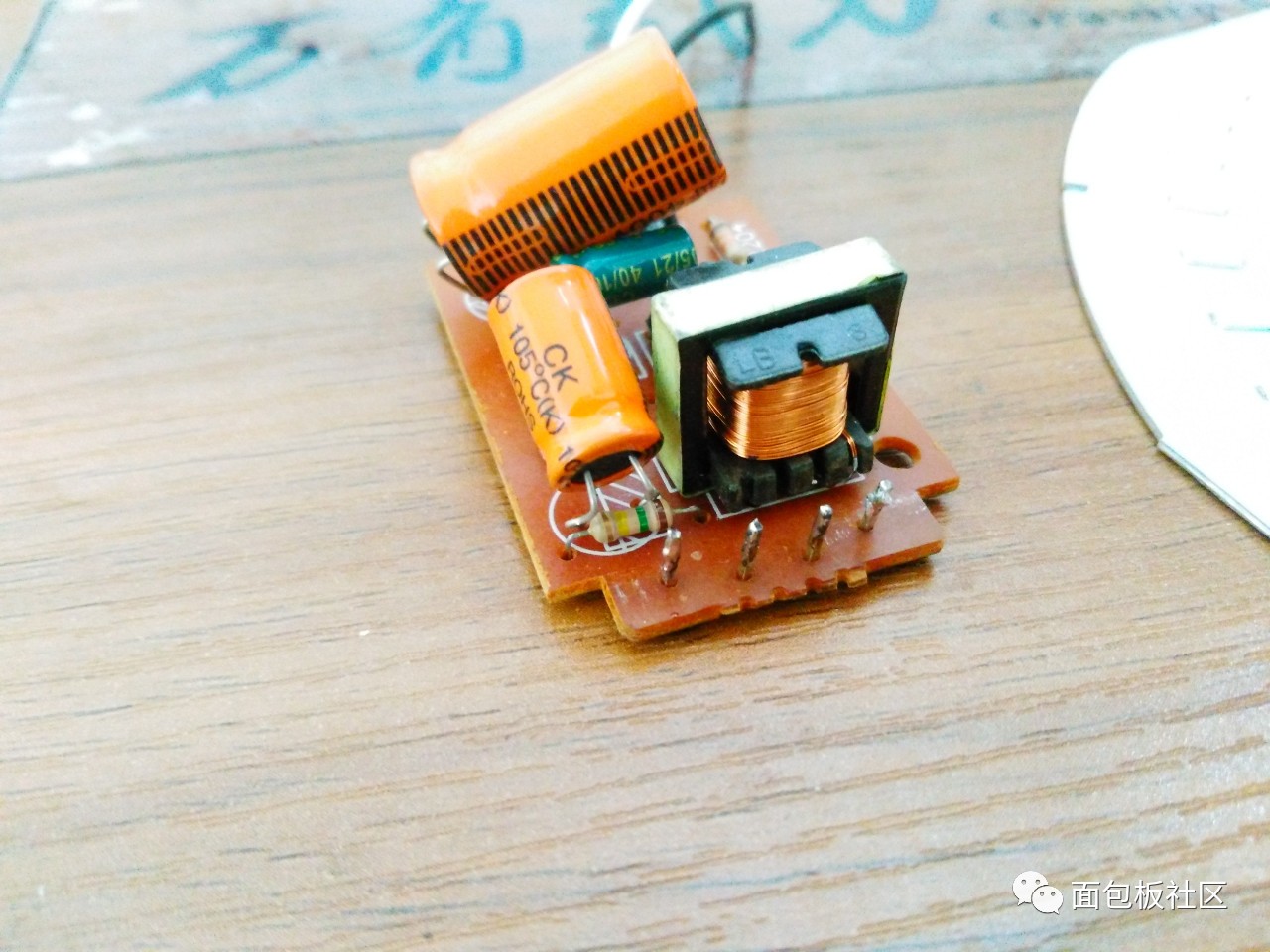
Junction
Remove the back of the control panel:
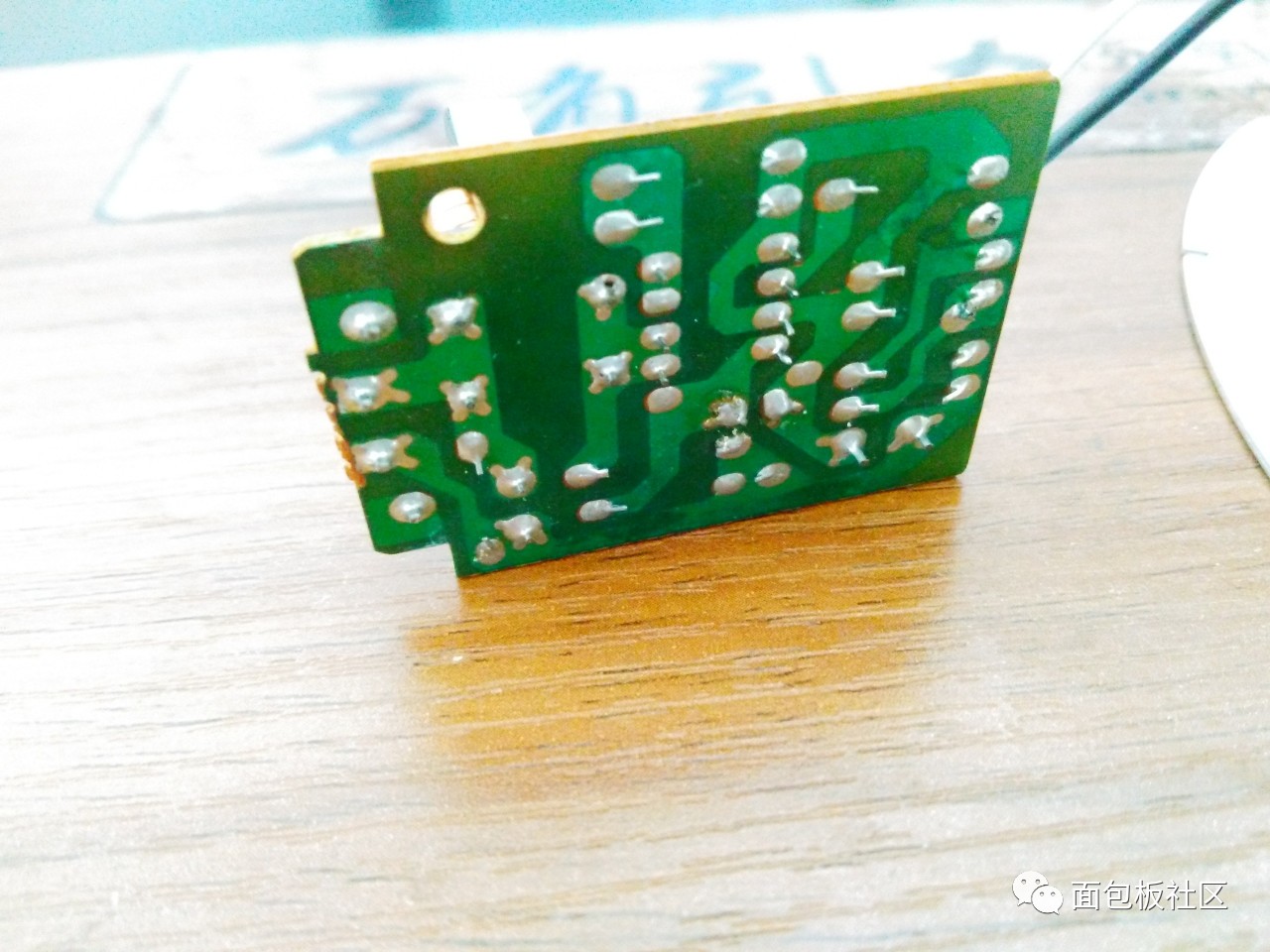
back
The silkscreen above can be clearly seen:
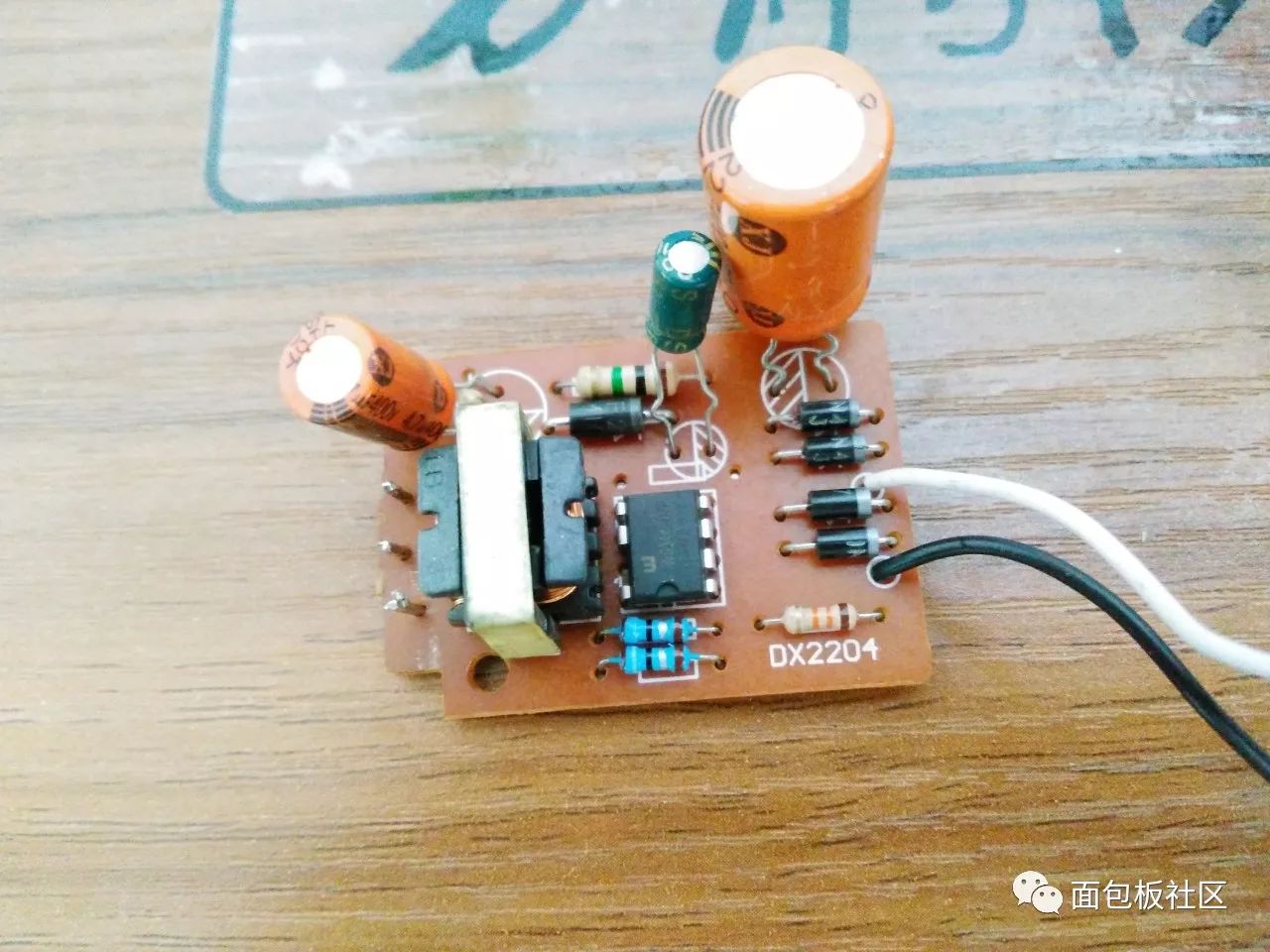
Components & Screen Printing
At this point, the disassembly is complete, and then the principle is analyzed:
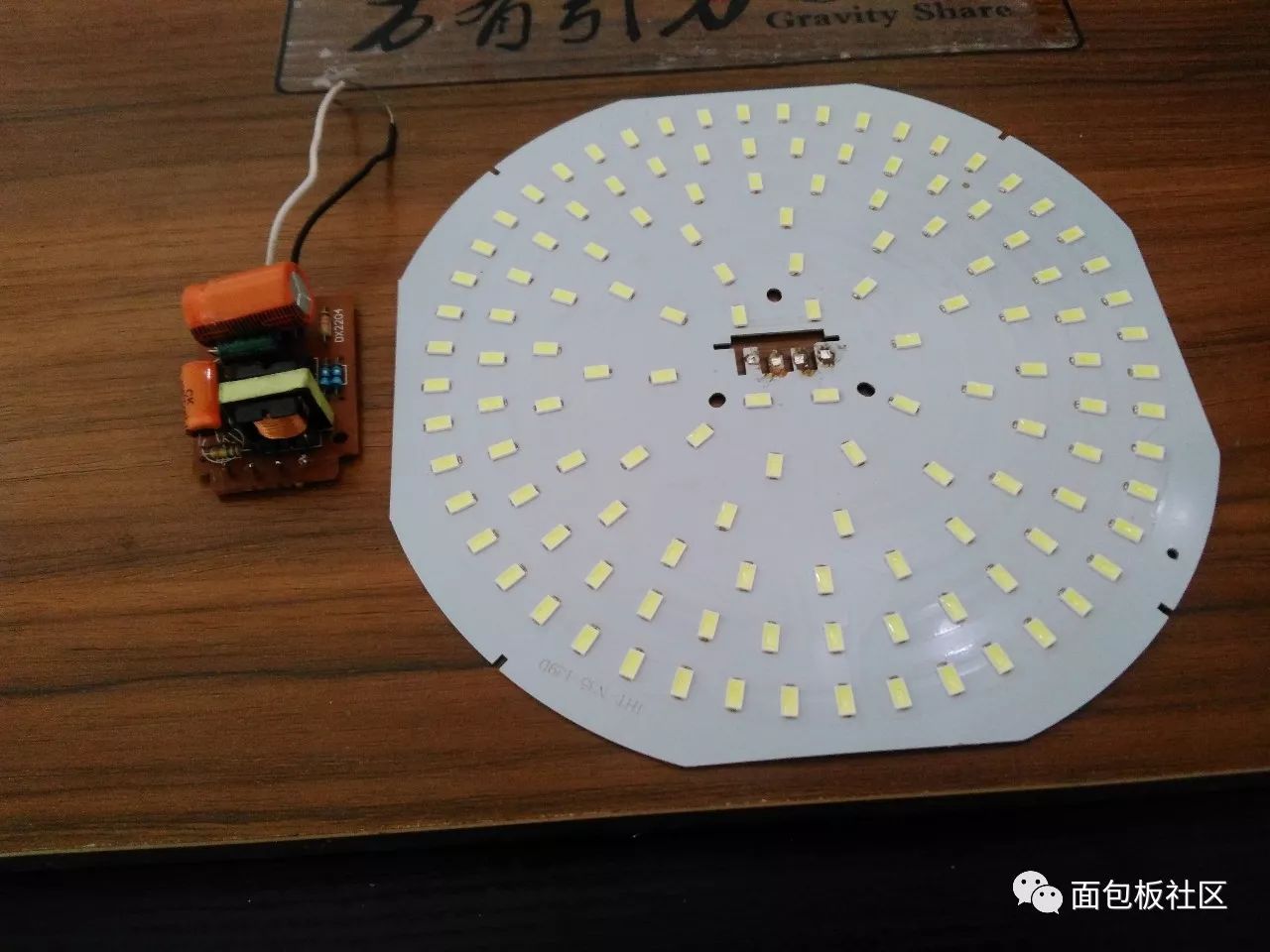
Disassembly completed
Third, the principle of disassembly
The WS3442 is a high precision LED constant current control IC for non-isolated step-down LED power systems for a full range of AC voltage inputs or DC voltage inputs from 12V to 500V. The main application areas are LED bulbs and lamps.
WS4332 chip application guide: 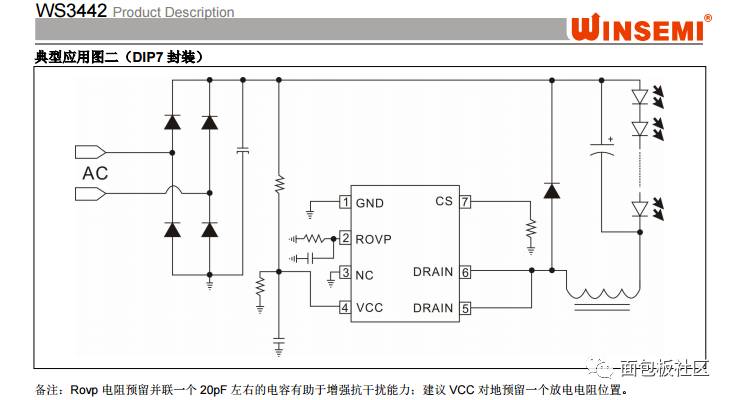 P14 WS4332 application
P14 WS4332 application
The principle of this LED energy-saving lamp is mainly to use WS4332 as the control chip, and the 220V input AC power is filtered and converted into DC voltage to supply 43 groups of LEDs in series to supply power. The combination method is 3 parallels and 43 sets are connected in series: The following is a combination diagram of this LED energy-saving lamp: 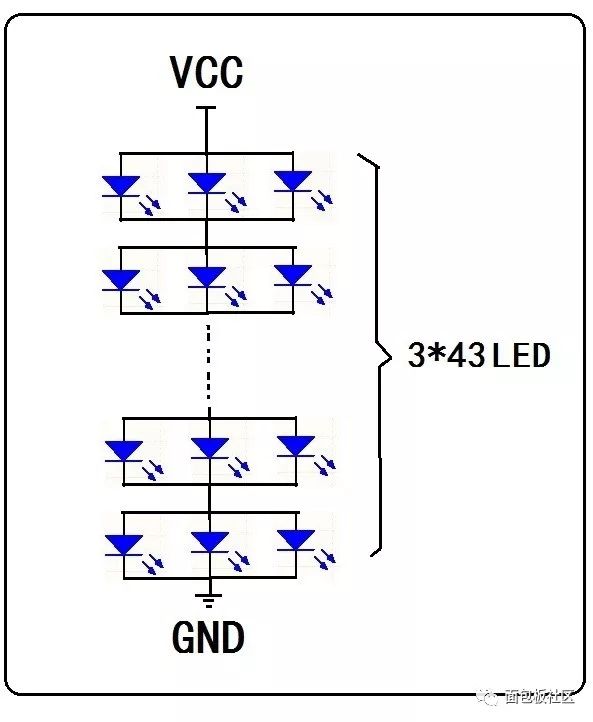 P15 LED combination
P15 LED combination
Fourth, the dismantling
After the disassembly of the LED energy-saving lamp, it can be seen that the principle is not complicated. The LED energy-saving lamp controlled by WS4332 is simple in design, and the constant current effect can be realized by adjusting the external resistance value according to the current voltage of different LED lamp groups. The voltage of a single LED lamp bead used in this LED energy-saving lamp ranges from 3.0V to 3.5V, and the power is about 0.5W. According to the calculation of 129*0.5≈64.5W, it meets its nominal power of 60W.
Absolute rotary Encoder measure actual position by generating unique digital codes or bits (instead of pulses) that represent the encoder`s actual position. Single turn absolute encoders output codes that are repeated every full revolution and do not output data to indicate how many revolutions have been made. Multi-turn absolute encoders output a unique code for each shaft position through every rotation, up to 4096 revolutions. Unlike incremental encoders, absolute encoders will retain correct position even if power fails without homing at startup.
Absolute Encoder,Through Hollow Encoder,Absolute Encoder 13 Bit,14 Bit Optical Rotary Encoder
Jilin Lander Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.jilinlandermotor.com