The Industrial Internet of Things spans many important areas and has revolutionized manufacturing. The main factors determining the level of industrial Internet of things are high positioning, high transmission, and high performance. Combining sensing, communication and data analysis, the Industrial Internet of Things can maximize operational efficiency. Manufacturing will account for the largest proportion of the IIoT market.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) continues to have a fever, and the global manufacturing industry is making a new wave of changes. Through wireless communication technology, positioning, sensing and other technologies, we will create a complete design that can increase production capacity and yield, meet the demand for customization and speed of industrial production lines, and enhance the resilience and intelligence of factories.
Whether it's called Industrial IoT or Industry 4.0, through the combination of sensing, communication and data analysis, Industrial IoT can dramatically improve processes and efficiencies for manufacturing, transportation, fleet management, mining and agriculture. The industry brings new changes.
While the industry is currently focusing on getting more raw data, then analyzing it and providing it to key decision makers, it now pays more attention to location and time information. This trend shifts because the “rich environment†message will provide exciting opportunities for program developers and system designers in IoT applications.
For example, instead of simply using the monitoring sensors of the tire pressure or suspension system to detect dangerous bumps or potholes on the road, if this data is combined with precise position information and provided to other vehicles in the fleet, This dangerous location can be avoided, reducing damage to the entire fleet (Figure 1).
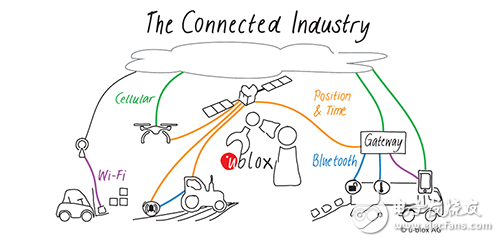
figure 1
The Industrial Internet of Things spans many important areas, all of which benefit from more precise and rich environmental information due to accurate location and time.
Currently, the fleet has been able to monitor the various states of the vehicle using Electronic Logging Devices (ELD). Important parameters include mileage, location, stop, engine usage, and driving hours. Since the pressure, fuel and temperature sensors have been integrated into the tire and Engine Control Units (ECU) to track parameters such as vibration, humidity and displacement, the overall condition of the vehicle can be monitored in real time so that Repairs should be made early before a serious failure occurs. The main difference now is that it requires a combination of precision positioning and secure data communication technology to further monitor the vehicle.
In the agricultural sector, the Industrial Internet of Things helps ensure a global food supply. According to forecasts, by 2020, there will be 9.1 billion people worldwide, using networked sensors to track temperature, soil conditions, sunshine and humidity, and provide the data needed for optimal land use. Accurate location services and real-time information communication enable farmers to ensure that crops are harvested quickly and efficiently at the optimal time.
Of course, if the data, time and location are incorrect, or if communication is not possible due to unreliable, high latency, or unsafe system setup, then all of these advantages will not work. Inaccurate locations and delays of 150 microseconds or longer may be acceptable for consumer devices and home networks, but for industrial applications, maximum performance, durability, security, and reliability are critical.
In addition, the requirements for positioning accuracy have driven multiple standards organizations and innovation companies to re-examine global navigation satellite services (GNSS) such as GPS, Beidou and GLONASS, as well as short-range radio and cellular technology to work together. Probably provide the most accurate time and location information.
For example, the angle-of-arrival (AoA) and Angle-of-departure (AoD) analysis of the Bluetooth signal, and the TIme-of-flight (ToF) analysis using the access point signal, Wi-Fi network signal patterning algorithm (FingerprinTIng) and other technologies have been adopted at present, in addition, ultra-wideband (UWB) signal technology has re-emphasized in positioning applications.
Honeycomb technology is moving towards diversification. Honeycomb technology has always focused on higher data rates in response to the needs of multimedia applications, but now narrow-band IoT (NB-IoT) has gained attention, enabling indoor and outdoor, low-power in licensed bands. Sensor communication application.
Research firm MarketandMarkets predicts that from 2015 to 2020, the industrial IoT market will grow at a compound growth rate (CAGR) of 8.03% per year and will reach a market size of $151 billion.
The report also pointed out that advances in semiconductor technology, cloud computing, IPv6 standardization, and government support are all important contributors to IIoT. But the real driving force comes from manufacturing, which is expected to account for the largest proportion of the IIoT market.
Key areas of benefit for smart factories include product lifecycle management, electronics, materials and mining, field equipment, and Machine Vision.
The report points out that for most existing manufacturers, energy producers and agricultural producers, the initial benefits of adopting IoT are mainly due to the cost savings and process improvements mentioned above, as well as the potential to promote new revenue sources and strengthen Employee productivity and working conditions. In particular, the report also states that UAVs can be used to patrol pipelines to minimize exposure to hazardous environments (Figure 2).
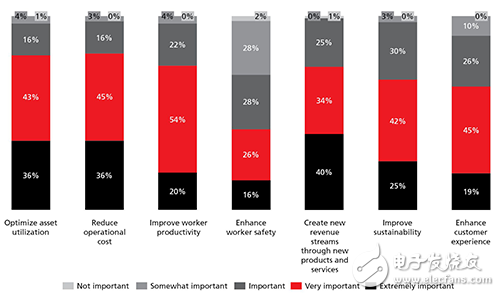
figure 2
Reducing operating costs, increasing productivity, and creating new revenue streams are just three of the many reasons to drive the development of industrial IoT. This trend can also bring more imagination and possibilities to designers and businesses.
8 Inch Coaxial Speaker,Professional Coaxial Speaker,Ferrite Coaxial Speaker,Pro Audio Coaxial
Guangzhou BMY Electronic Limited company , https://www.bmy-speakers.com