Voltage, also known as potential difference or potential difference, is a physical quantity that measures the energy difference of a unit charge due to a difference in potential in an electrostatic field. Its size is equal to the work done by the unit's positive charge due to the electric field force moving from point A to point B. The direction of the voltage is defined as the direction from the high potential to the low potential. The international unit system of voltage is volts (V), and the commonly used units are millivolts (mV), microvolts (μV), and kilovolts (kV). This concept is similar to the “water pressure†caused by the water level. It should be pointed out that the term "voltage" is generally used only in circuits, and "potential difference" and "potential difference" are generally applied to all electrical phenomena.
Voltage classification:By size
Voltage can be divided into high voltage, low voltage and safe voltage.
The difference between high and low voltage is: based on the voltage value of the electrical equipment to ground. Voltages higher than or equal to 1000 volts to ground are high voltages. Low voltage to ground voltage less than 1000 volts.
The safe voltage refers to the voltage that the human body contacts for a long time without the risk of electric shock. According to the national standard "GB3805-83", the safety voltage stipulates a series of voltages supplied by a specific power supply for preventing electric shock. China has specified the following five levels of industrial frequency safety voltage: 42V, 36V, 24V, 12V and 6V.
By function
Impedance voltage
Definition of term: A winding in a two-winding transformer is short-circuited, and the voltage at the rated frequency is applied to the other winding, and the value of the applied voltage at which the rated current flows is caused to flow. In the case of a multi-winding transformer, except for a pair of tested windings, the remaining windings are opened, and the value of the applied voltage at which the rated current corresponding to the smaller rated winding in the pair of windings flows is caused to flow therein. The impedance voltage of each pair of windings refers to the value at the corresponding reference temperature and is expressed as a percentage of the rated voltage value of the applied voltage winding.
Impedance voltage calculation method: When the secondary winding of the transformer is short-circuited (steady-state), the voltage applied by the primary winding flowing through the rated current is called the impedance voltage Uz. Usually Uz is expressed as a percentage of the rated voltage, ie, uz=(Uz/U1n)×100%åŒ Potential: u=4.44×f×B×At, V where: B—the magnetic density in the core, and the effective cross-sectional area of ​​the TAt—core , Square meters can be converted into commonly used formulas for transformer design calculations:
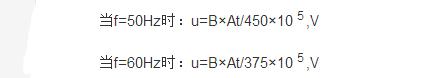
If you already know the phase voltage and the number of turns, the åŒ potential equals the phase voltage divided by the number of turns.
2. Medical voltage
The voltage referred to in the electrocardiogram refers to the distance between two horizontal lines on the ECG drawing. Commonly used to determine the amplitude of ECG. Units are usually expressed in mm or mV. The value of the voltage is related to the adjustment of the calibration voltage. If a standard voltage of 1 mV is input and the baseline is shifted by 10 mm, the distance between the two thin horizontal lines is 1 mm and the voltage is 0.1 mV. When measuring the amplitude of the electrocardiogram, the voltage quotient is significant.
The role of voltage:Everyone knows that water can flow in a pipe because there is a pressure created by the difference between a high water level and a low water level, and water can flow from a high place to a low place. The tap water used in the city can be discharged from the pipe as soon as the water gate is opened. It is also because the tap water tower is higher than the ground, or because of the pressure difference caused by pumping the water. Electricity is also the same, so current can flow in the wire, also because there is a difference between high potential energy and low potential energy in the current. This difference is called potential difference, also called voltage. in other words. In the circuit, the potential difference between any two points is called the voltage of these two points. The voltage is indicated by the symbol "U". The level of voltage is generally expressed in units of volts, abbreviated as "V". The high voltage can be expressed in kilovolts (kV) and the low voltage can be expressed in millivolts (mV). Voltage is the cause of the current.
The role of voltage, so that a certain circuit in the current
The conversion relationship between them is:
1 kV = 1000 volts (V)
1 volt (V) = 1000 millivolts (mV)
The kilovolt is greater than volts is greater than millivolts and the rate of advance is 1000.
Voltage, like water pressure, water pressure can make static water flow in a certain direction, then the voltage is a physical quantity that can make the electrons in the conductor move in a certain direction. The definition of it can be simply understood as such. If physics is just touching (perhaps not just touching it), it must be learned. The best way is to communicate and learn, learn from each other, and even be interested, you can learn! The relationship between voltage, current, and resistance is Ohm's law (Ohm's theorem only applies to purely resistive circuits or circuits that convert electricity to internal energy, such as electric heating wire, but the motor is not applicable) Voltage = resistance * current U = RI current = Voltage/Resistance I=U/R Resistor=Voltage/Current R=U/I Electrical Energy=Current*Voltage*Power On Time W=I*U*t Note that the common mistake in this formula is the phrase “Resistance vs. Conductor The two voltages are proportional to each other and inversely proportional to the current." This is wrong. Resistance is the inherent characteristic of the conductor. It is only related to the length, cross-sectional area, material and temperature of the conductor (contacts them in the middle school), and the voltage Nothing about current.

Voltage drop, also known as voltage or potential difference, is expressed as U, in volts (V), which is the physical quantity that describes the power of an electric field to move a charge to do work.
. When the charge flows, the energy of the charge is released in the circuit, and the connected components in the circuit and circuit absorb the energy of the charge. After energy absorption, the energy released by the charge itself becomes smaller, and people use the voltage drop to measure the ability of the charge to release energy in the circuit. When a current flows through the circuit, a certain voltage drop will occur in each segment of the circuit, and the voltage drop represents the amount of electrical energy that the charge flows through the small segment (or is expressed as absorbed by the small segment of the circuit).
Voltage drop is referred to as voltage. The voltage between two points refers to the work done by the positive charge of the unit under the action of the power supply. The unit of voltage is the same as the electromotive force (Volt for short, denoted by the English letter V).
The formula for the voltage drop between two points: U=W/q
In the formula, W——work done by electric force to move electric charge, q——positive charge that is moved by electric force
The reference direction of the voltage drop is indicated by the "+" "-" polarity or the double subscript. The actual direction of the voltage is defined as the direction in which the electric field force moves the positive charge to do work, from the high-potential ("+" polarity) to the low-potential ("-" polarity), which is the direction in which the potential decreases.
The voltage drop can also be called potential difference. When the potential at a certain point is zero, the voltage at any point in the circuit at this reference point is the potential (U) at that point. The potential difference between any two points is also the voltage drop between two points.
Voltage drop causes:For power devices, such as generators, transformers, and other power cables, when the transmission distance is long, for example 900m, the “voltage drop†of the first library's network voltage should be considered. Otherwise, the cable procurement, installation, etc. Because the pressure drop was not taken into consideration, the equipment could not be started normally, resulting in engineering losses.
The voltage drop of the power line is due to the resistance of the conductor. Because of this, no matter what kind of material (copper, aluminum) the conductor will cause a certain voltage loss of the line, and this loss (voltage drop) is not greater than 5% of its own voltage is generally not generated on the electric drive of the line Consequences. For example, for a 380V line, if the voltage drop is 19V, that is, the circuit voltage is not lower than 361V, there will be no big problem.
Voltage drop â–³U=IR<5%U to meet requirements 220*5%=11V380*5%=19V
Voltage and voltage drop are not a concept.
Voltage, also known as potential difference or potential difference, is a physical quantity that measures the energy difference of a unit charge due to a difference in potential in an electrostatic field. Its size is equal to the unit of positive charge due to the action of the electric field force to move from point A to point B. The direction of the voltage is defined as the direction from the high potential to the low potential.
Current through the conductor (or electrical appliances), will be subject to some resistance, but under the influence of the voltage, the current can overcome this resistance through the conductor (or use electrical appliances), but unfortunately, through the series resistance (or After using electrical appliances, the voltage is no longer as high as it used to be. It has fallen. And the greater the resistance, the greater the voltage difference changes. So the current flowing through a resistor (or appliance), which produces a voltage difference, is called a "voltage drop."
There is a difference between voltage and voltage drop, and there are links.
The voltage is the cause of the free movement of the conductor in the conductor to form a current. There is a voltage across the conductor and there will be current in the conductor. This is from the formation of currents,
When there is current in the circuit, the potential at each point in the circuit is reduced along the direction of the current in different positions of the circuit, and the decrease in the potential across a conductor is the voltage drop, that is, the current in the conductor. There is a potential difference at both ends of the conductor, which is the value of the potential drop. This is the result of the work done by the current. Current works, the potential drops.
57 Series Centronic Connectors
Current Rating:5A
Dielectric Withstanding Voltage:1000V for one minute
Insulation Resistance:1000MΩ Min.(at 500V DC)
Contact Resistance:35mΩ Max.
Temperature:-55°C to +105°C
57 Series Centronic Connectors
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.pcbsocket.com