As a new generation of mobile communication technology, the rapid development of 5G technology is in line with the traditional manufacturing enterprise's intelligent manufacturing transformation needs for wireless network applications. The three major scenarios defined by 5G technology not only cover traditional applications such as high bandwidth and low latency, but also It can also meet the needs of device interconnection and remote interactive applications in industrial environments. This WAN full coverage feature makes it possible for enterprises to build a unified wireless network.
First, the development of mobile communication technologyLooking back on the development of mobile communication technology, the first generation used analog technology, which can only support regional and distance-limited voice calls; the second generation realized digital voice communication, enabling simple voice and text-like interactions, such as SMS and The third generation is known as 3G technology. It is characterized by multimedia communication and can support voice, text and video interaction. However, due to limited bandwidth, it is difficult to ensure smooth effect when performing large amounts of data interaction, such as video interaction. The fourth generation is the 4G technology being built, and the communication speed is greatly increased, marking the era of entering the wireless broadband.
From the base station test results of current telecom service providers, the speed of 5G will be faster than 4G and the power consumption will be lower, and the theoretical bandwidth will exceed 10G per second. This guarantees that you can download a high-definition movie in one second, while 4G takes at least 10 minutes. It is precisely because of this unique advantage that the industry generally believes that 5G will play an important role in promoting the smart industry, driverless cars, VR and the Internet of Things.
Currently, the 5G standard has not yet been determined. AT&T President Smith believes that the definition of 5G may be determined in 2018, and the official 5G standard will be written by the United Nations Mobile Communications Alliance in 2019. The 5G standard will define which wireless technologies can be called 5G, and what features are available in 5G.
Second, the three major scenes defined by 5GIn 2016, the PolarCode scheme promoted by China was determined by the international wireless standardization organization 3GPP as the control channel coding scheme of the eMBB scenario, and the uplink and downlink short code schemes of the data channel belonged to the Qualcomm LDPC code. eMBB enhances mobile broadband and is one of the three major 5G scenarios defined at the 3GPP conference. Huawei's PolarCode channel coding technology is just one of many core technologies of 5G. In addition to eMBB, the 5G scene also includes mMTC and URLLC.
eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband): It is mainly for high-traffic mobile broadband services such as 3D/Ultra HD video. In addition to spectrum development technologies below 6 GHz, eMBB will also develop spectrum above 6 GHz. Small base stations will be important equipment for the development of eMBB. Due to the current spectrum below 6 GHz, most of them are based on the traditional network mode developed by large base stations. Compared with the millimeter wave technology with spectrum above 6 GHz, small base stations are needed. To drive the speed faster.
mMTC (Massive Machine Communication): Mainly for large-scale IoT business. mMTC will develop in the frequency band below 6GHz, which will be applied to large-scale Internet of Things. The currently visible development is NB-IoT. In the past, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Bluetooth, etc., are relatively small-scale technologies for home use. The return lines are mainly based on LTE. Recently, with the coverage of NB-IoT and LoRa, which are widely covered, it is expected. Let the Internet of Things develop more broadly.
URLLC (Super Reliable Low Latency): Mainly for services such as driverless, industrial automation that require low latency and high reliability. In smart factories, because a large number of machines have built-in sensors, these processes from sensors, back-end networks, and instructions to the machine itself, if transmitted over the existing network, there will be obvious delays that may lead to safety. ACCIDENT. In view of this, URLLC pushes the target of network latency down to less than 1 millisecond.
Third, 5G support industrial applicationsInternet of Things
With the advancement of the intelligent transformation of the factory, the Internet of Things as a key supporting technology for connecting people, machines and equipment is receiving high attention from enterprises. This demand has greatly stimulated the development of 5G technology while promoting the application of IoT applications. Faced with complex industrial interconnection needs, 5G technology needs to adapt to different industrial scenarios and meet most of the connectivity needs of the Internet of Things. Therefore, 5G and the Internet of Things are complementary. The Internet of Things application relies on 5G to provide wireless connectivity solutions for different scenarios. The maturity of 5G technology standards also requires the stimulation and promotion of IoT application requirements.
In the process of pushing the Internet of Things, the 5G three scenes can support different functional application requirements. For example, eMBB can support high-bandwidth application scenarios such as remote video surveillance and video conferencing; mMTC can meet the data connection and transmission requirements of a large number of low-power embedded terminals. URLLC can lower the network latency to less than 1 millisecond to support the many indicators and requirements of the system and equipment for real-time data transmission during industrial automation control.
2. Industrial automation control
Automation control is the most basic application in a manufacturing plant, and the core is a closed-loop control system. Each sensor is continuously measured during the control cycle of the system, and measurement data is transmitted to the controller to set the actuator. The typical closed-loop control process cycle is as low as the ms level, so the delay of the system communication needs to reach the ms level or even lower to ensure the precise control of the control system, and the reliability is also extremely high. If the production process is too long, or the control information is wrong during data transmission, the production may be shut down, which will cause huge financial losses.
The 5G provides a very low-end, high-reliability, massively connected network, making closed-loop control applications possible via wireless network connections. Based on the measured capability of Huawei 5G: the air interface delay can reach 0.4ms, the single cell downlink rate reaches 20Gbps, and the cell can support up to 10 million+ connections. It can be seen that only 5G networks in the mobile communication network can meet the requirements of the closed-loop control for the network.
3. Logistics tracking
In the current machine-to-machine market, the application will include personnel tracking and high-priced goods in transit. But (more) high connection costs limit the growth of the market. 5G is expected to provide additional advantages in terms of deep coverage, low power consumption and low cost (economies of scale) and as a 3GPP standard technology. The improvements provided by 5G will include optimizing logistics in a wide range of industries, improving worker safety and improving the efficiency of asset positioning and tracking to minimize costs. It will also expand its capabilities to enable dynamic tracking of a wider range of in-transit merchandise. As online shopping increases, asset tracking becomes even more important.
In terms of logistics, from warehouse management to logistics and distribution, wide coverage, deep coverage, low power consumption, large connections, and low-cost connection technologies are required. In addition, the end-to-end integration of virtual factories spans the entire lifecycle of a product, connecting a wide range of sold merchandise, as well as low-power, low-cost and wide-coverage networks, horizontal integration within or between enterprises. There is also a need for ubiquitous networks, and 5G networks are well suited to meet these needs.
4. Industrial AR
In the future production process of smart factories, people will play a more important role. However, due to the high degree of flexibility and versatility of the factory in the future, this will place higher demands on the factory floor staff. To quickly meet the needs of new tasks and production activities, Augmented Reality AR will play a key role in the smart manufacturing process for scenarios such as monitoring processes and production processes. Step-by-step instructions for production tasks, such as manual assembly process guidance; remote expert business support, such as remote maintenance.
In these applications, the auxiliary AR facility requires maximum flexibility and portability for efficient maintenance. Therefore, the device information processing function needs to be moved up to the cloud, and the AR device only has the function of connecting and displaying, and the AR device and the cloud are connected through the wireless network. The AR device will obtain the necessary information (for example, production environment data, production equipment data, and troubleshooting guidance information) in real time through the network. In this scenario, the display content of the AR glasses must be synchronized with the motion of the camera in the AR device to avoid visual range out of step. Usually, from the visual movement to the AR image response time is less than 20ms, there will be better synchronization, so it is required that the cloud backhaul from the camera to the cloud to the AR display content needs less than 20mms, except for screen refresh and cloud processing. If the delay is required, the two-way transmission delay of the wireless network needs to be within 10 ms to meet the real-time experience. The delay requires that the LTE network cannot be met.
5. Cloud robot
In the smart manufacturing production scenario, robots need self-organizing and synergistic capabilities to meet flexible production, which brings the need for robots to cloud. Compared with traditional robots, cloud-based robots need to be connected to the cloud's control center through a network, based on a platform with ultra-high computing power, and real-time computing control of the manufacturing process through big data and artificial intelligence. Cloud computing robots move a lot of computing functions and data storage functions to the cloud, which will greatly reduce the hardware cost and power consumption of the robot itself. And in order to meet the needs of flexible manufacturing, robots need to meet the requirements of free movement. Therefore, in the process of clouding robots, wireless communication networks are required to have extremely low latency and high reliability.
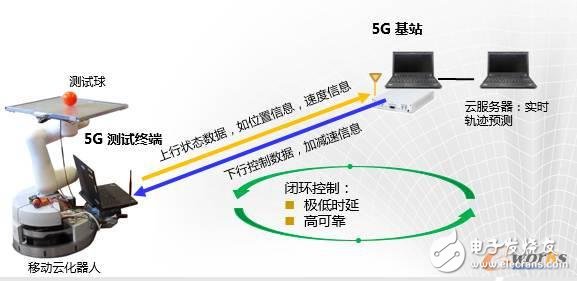
5G network and cloud robot
The 5G network is the ideal communication network for cloud-based robots and the key to enabling cloud-based robots. The 5G slicing network provides end-to-end customized network support for clouded robot applications. 5G networks can achieve end-to-end communication delays as low as 1ms, and support 99.999% connection reliability. The powerful network capability can greatly meet the challenges of cloud robots for delay and reliability.
to sum up
5G technology has become a key enabling technology to support the transformation of intelligent manufacturing. 5G technology can use three major scenarios to connect a wide range of scattered people, machines and equipment to build a unified Internet. Due to its real-time and high reliability, 5G technology can be used not only in industrial scenarios, but also to support personal mobile Internet applications. The development of 5G technology can help manufacturing enterprises to get rid of the confusing application state of wireless network technology in the past, which has positive significance for promoting the implementation of industrial Internet and deepening the transformation of intelligent manufacturing.
Guangzhou Yunge Tianhong Electronic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.e-cigaretteyfactory.com