A key and pivotal component in the process of converting mechanical energy from electrical energy. For a generator, it is a component that generates an electromotive force, such as a rotor in a DC generator, a stator in an alternator; for an electric motor, it is a component that generates electromagnetic force, such as a rotor in a DC motor.
The armature is the part of the motor that is equipped with a coil, and the relative movement of the coil to the magnetic field. In the generator, an induced electromotive force is generated in the coil that is forced to rotate to generate electricity. In an electric motor, the energized coil is subjected to an ampere force in a magnetic field to cause it to rotate in a magnetic field.
The armature winding is divided into two categories: DC armature winding and AC armature winding. They are used for DC motors and AC motors, respectively.
The armature includes an armature core and an armature winding. The armature winding is a circuit part of the DC motor, and is also a part that induces an electric potential and generates electromagnetic torque for electromechanical energy conversion (the generator is mechanical energy converted into electric energy). The armature core is both a part of the main magnetic circuit and a supporting member of the armature winding, and the armature winding is embedded in the slot of the armature core.
The principle of the induced armature of the DC motor and the AC motor is roughly the same. The current in the armature winding of the DC motor is also AC, and the output through the commutator is DC.
The AC motor is divided into an induction motor (asynchronous machine) and a synchronous motor. The induction motor is divided into a squirrel cage rotor and a wound rotor according to the rotor structure. The induction motor generates a magnetic field by the stator winding, and the rotor winding performs electromechanical energy conversion.
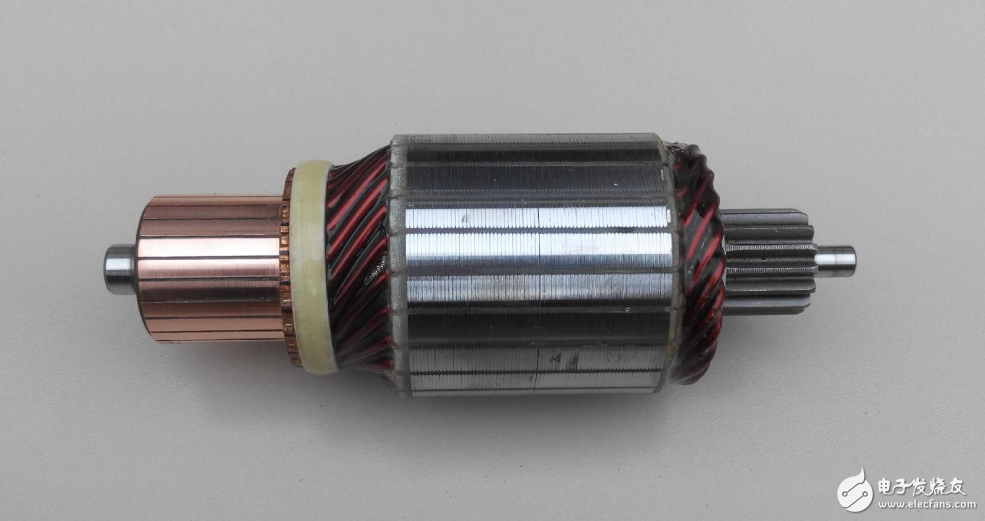
The rotor is a scientific term. Refers to the rotating body supported by the bearing. An object such as an optical disc that does not have a rotating shaft itself can be regarded as a rotor when it is rigidly connected or attached.
According to the ISO standard, a rotating body supported by a bearing is called a rotor. The rotor is mostly the main rotating part in power machinery and working machinery. Typical rotors include turbine mechanical rotors, motor rotors, rotors for various pumps, and rotors for turbo compressors. When the rotor rotates at a certain speed, it will deform greatly and cause resonance. The speed at which resonance occurs is called the critical speed of the rotor.
In engineering, a rotor whose working speed is lower than the first-order critical speed is called a rigid rotor, and a rotor larger than the first-order critical speed is called a flexible rotor. Since the rotor performs a high-speed rotational motion, balance is required. Static balance is mainly used to balance the inertial force of the disc rotor. The dynamic balance of the rigid rotor can balance the inertial force and the inertial force couple through a universal balancing machine, eliminating the vibration of the rotor on the elastic support. The dynamic balance of the flexible rotor is more complicated, and it is distinguished from the principle by the vibration mode balance method and the influence coefficient method.
The rotor is difficult to change direction, high speed, and various faults. Common faults include commutator damage, bearing damage, vane damage, brush wear, and rotor winding burnout.

The armature winding is simply said: in an AC synchronous motor, the armature is the stator of the AC synchronous motor; in the DC motor, the armature is the stator of the DC motor; the induction motor (asynchronous motor) has no armature, only the stator and the rotor.
The armature is present with respect to the magnetic pole. The armature and the magnetic pole are the main components of the synchronous motor and the DC motor. The magnetic pole is the part that generates the magnetic field, and the armature is the part that generates the induced electromotive force, passes the current, and generates the electromagnetic torque. They are all composed of a core and a corresponding winding.
The armature current of the AC synchronous motor and the DC motor is not necessarily related to the magnetic pole current. The armature winding is responsible for inducing the electromotive force and current, and the magnetic pole (rotor) is responsible for generating the magnetic field.
The stator winding and the rotor winding of the induction motor (induction motor) both induce an electromotive force, both of which pass current, and the rotor current follows the change of the stator current, but there is no synchronization, so it is called an asynchronous motor. No winding of the induction motor is specially developed to generate a magnetic field. Therefore, the induction motor has only the distinction between the stator and the rotor, and there is no distinction between the armature and the magnetic pole.
portable hand pump,Marine portable hand pump,portable hand water pump
Taizhou Jiabo Instrument Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jbcbyq.com