The soft robotic sleeve twists and compresses in synchrony with the beating heart, enhancing cardiovascular function with reduced heart failure. Unlike existing devices that assist in heart function, Harvard's soft robotic sleeve does not directly touch the blood. This reduces the risk of blood clotting and eliminates the need for patients to take potentially dangerous blood thinners. The device can one day bridge the patient for transplantation or help the heart to recover and recover. Let's take a look at the related content with the embedded Xiaobian.
"This study shows that more and more areas of soft robots can be applied to clinical needs and have the potential to reduce the burden of heart disease and improve the quality of life of patients," said the author and former Dr. Ellen Roth. Cut it. D. Harvard University, John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Science (SEAS) and Wyss Bio-Inspired Engineering College. Roche is currently a postdoctoral fellow at the National University of Ireland.
The study was published in Science TranslaTIonal Medicine and was developed in collaboration with SEAS, the Wyss Institute and Boston Children's Hospital.
“This work represents an exciting proof of concept for this soft robot, demonstrating that it can safely interact with soft tissue and lead to improved heart function. We envision many other future applications where these devices can be in vivo And in vitro mechanical therapy," said Conor Walsh, senior author of the paper, John L. Loeb, associate professor of engineering and applied sciences at SEAS, and the Wyss Institute, a core faculty member.
There are 41 million people worldwide suffering from heart failure. Today, some treatment options are mechanical pumps called ventricular assist devices (VAD) that pump blood from the ventricle into the aorta and heart. Although VAD continues to improve, patients still have a high risk of thrombosis and stroke.
In order to create a new device that won't come into contact with blood, Harvard researchers are inspired by the heart. The thin silicone sleeve uses a flexible pneumatic actuator placed around the heart to mimic the outer muscle layer of the mammalian heart. The actuator twists and compresses the sleeve so that it moves like a beating heart.
The device is connected to an external pump that uses air to power the soft actuator.
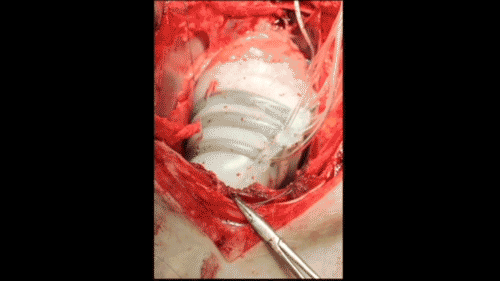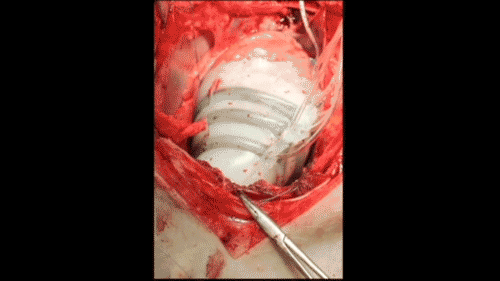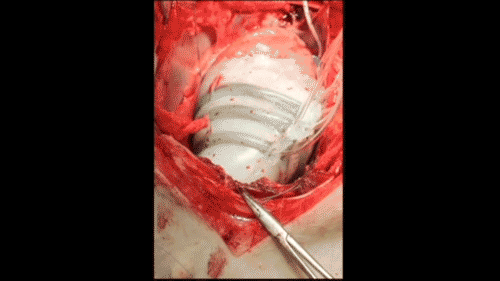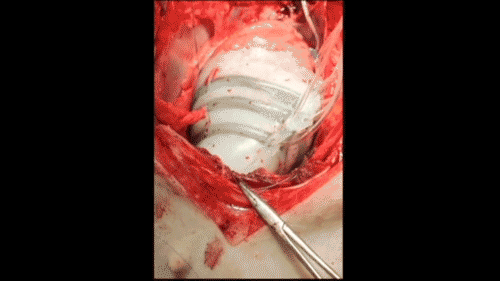
Roche said that the sleeves can be customized for each patient. For example, if the patient has more weakness on the left side of the heart, the actuator can be adjusted to provide more help there. As the patient progresses, the pressure on the actuator will increase or decrease over time.
Using a suction device, a combination of suture and gel interface attaches the cannula to the heart to aid friction between the device and the heart.
SEAS and Wyss engineers worked with surgeons at Boston Children's Hospital to develop the device and determine the best method for implanting and testing on animal models.
"Because of technical limitations, the heart has got rid of the idea of ​​developing heart compression, not blood-sucking VADs, but now with the advancement of soft-robot technology, it's time to turn things around," said heart-thinking surgeon and co-author Frank Pigula. The study served as clinical director of pediatric cardiac surgery at Boston Children's Hospital and is now a teacher at the University of Louisville and director of the Department of Pediatric Cardiac Surgery at Norton Children's Hospital. “Most heart failure patients still have some features, and one day robot sets can help their heart work well enough to restore their quality of life.â€
More research is needed before the sleeve is implanted in the human body, but this research is an important first step towards an implantable soft robot that can enhance organ function.
The Harvard Technology Development Office has filed a patent application and is actively seeking opportunities for commercialization.
"This research is very important now, because more and more people are suffering from heart attacks that eventually lead to heart failure," Roche said. “The soft robotic device is ideal for interacting with soft tissue and providing help to enhance functionality and even help healing and recovery.â€
European Socket Connector,30 Position European Socket Connector,Right Angle Male European Socket Connector,Male European Socket Connector
Dongguan Yangyue Metal Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.yyconnector.com