RapidIO is based on the packet-switched interconnect protocol and is mainly used as the internal interface of the system, such as inter-chip and inter-board communication, and the speed can be in the order of GB/S. Such as connecting processor, memory, memory mapped I / O devices. These devices may be network devices, memory subsystems, or general purpose calculations.

The RapidIO interconnect is a memory-oriented distributed memory system and subsystem. Such a system consists of multiple independent devices that use DMA to transfer data and transfer information between devices back and forth to maintain their consistency.
RapidIO is a definition of system interconnection. System concepts such as processor programming models, Cache, system reset, and interrupt programming models are beyond the scope of the RapidIO architecture. However, these features can be implemented using the resources provided in the RapidIO network. For example, the RapidIO architecture provides the necessary operations. To support the processor programming model, the scope is ordered from the overall storage to maintain strict consistency to weak ordering. Any references to these aspects in the RapidIO Architecture Specification are for illustrative purposes only, and subsequent specifications of RapidIIO may further define these system functions.
Although the RapidIO specification build is based on distributed memory systems, future versions will extend the capabilities of these interfaces and handle new topical content such as serial physical layer, global shared memory, interoperability, etc. These specifications are met. This specification's own independent package.
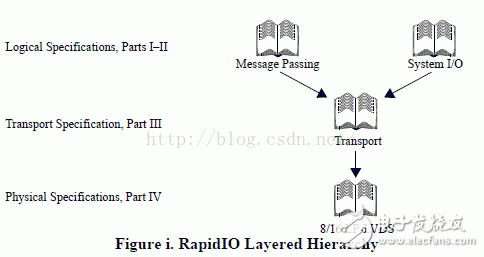
RapidIO uses a three-tier architecture: logic, universal transport layer, and physical layer.
1. Logical layer: Defines the operational protocols required by the endpoints, as well as the necessary transaction package formats through which the target operations are performed. The logical layers are not specific to a particular transport or physical interface, so they specify the bitstream format. Add the necessary bits of the logic layer to the lower layers in the layer architecture. Because the application uses different programming models, the RapidIO structure is split into sub-protocols to support them. The current RapioIO logical layer protocol includes:
System I/O Protocol Specification: Input and Output Logic Protocol
Messaging protocol specification.
Additional logical layer protocol specifications under different packages
2. Transport Layer: The Common Transport Layer Protocol describes the packet routing mechanism to pass RapidIO packets from one endpoint to another. The common transport layer is the public part of RapidIO.
3. Physical layer: defines the interface between the two devices and the packet transmission mechanism, flow control, and electrical performance parameters.
1.2 RapidIO feature set
RapidIO feature sets and protocols are based on general-purpose computing and embedded applications. The characteristics of each layer can be divided into three categories: functional aspects, physical aspects, and performance characteristics.
1.2.1 Logical layer featuresIf a large amount of non-correlated data is encapsulated in a packet, message transfer and DMA devices can improve interconnect efficiency. Therefore, the RapidIO packet format supports packets of different sizes because the messaging programming model is essentially an unrelated non-correlation. Shared memory model, in a RapidIO device, some parts of the memory space can only be accessed directly by a processor or a local device that controls the messaging interface.
The header is as small as possible to reduce the control load and the organization, packaging, disassembly and other operations of the package are faster and more efficient. As the data contained in a package increases, the efficiency of the package also increases. RapidIO supports data payloads up to 256 bytes. Messages are very important for embedded control applications, so support for large data domain changes and multi-packet messages.
Concurrent transmissions that allow multiple transactions in the system not only enable pipelined transactions on a single device, but also time-division interfaces between multiple devices. Without these features, most of the system pass rate will be wasted.
1.2.1.1 Functional characteristics
Many embedded systems are multiprocessor systems, not multiprocessing systems. To support distributed I/O and distributed processing requirements, especially in the network and routing markets, messaging or software-based coherent programming models are superior to traditional computer-type global shared memory programming models. RapidIO supports all of these programming models.
Both very large and very small systems support the same compatible package format to accommodate future expansions and changes in requirements.
Read-modify-write atomic operations are very useful for implementing synchronization between processors or other system components.
The RapidIO architecture supports 50-60bit addresses and also supports 34bit local addresses for smaller systems.
If a large amount of non-correlated data is encapsulated in a packet, message transmission and DMA devices can improve the efficiency of the interconnection, so the RapidIO packet format supports variable size packets.
Because the messaging programming model is essentially a non-correlated non-shared memory model, RapidIO assumes that certain parts of the memory space can only be accessed directly by a processor or a device that is local to that memory space. A remote device attempting to access this portion of memory must pass through a local device that controls the messaging interface.
1.2.1.2 Physical characteristics
The RapidIO package is defined to be independent of the width of the physical interface.
Protocol and packet formats are independent of physical interconnect structures, such as point-to-point links, bus types, multi-dimensional switched networks, dual serial connections, etc.
RapidIO does not depend on the bandwidth or latency of the physical architecture
Protocol processing out-of-order packet transmission and reception
Geographic addressing is not required in RapidIO, the identity of the device is independent of its geographic location, but the identifier can be assigned in other ways.
For proper operation, some devices have bandwidth and latency requirements, and RapidIO should not preclude the use of these limitations when implementing the system.
1.2.1.3 Performance characteristics
For web applications, messages are very important, so to increase efficiency, support varying size data fields and multi-package information.
The header is as small as possible to reduce the control cost, making the package more efficient in organization, packaging and disassembly.
Multiple transactions allow concurrency to prevent wasted system performance.
1.2.2 Transport layer characteristics1.2.2.1 Functional characteristics
System sizes can be large or small, but they are all the same or compatible package formats
Because RapidIO has only one transport protocol, compatibility in different specific implementations is assumed to exist.
The transport protocol is flexible and, therefore, adapts to future applications.
A package is always assumed to be from a source to a destination.
1.2.2.2 Physical characteristics
The transport layer definition is independent of the width of the physical interface.
Geographic addressing is not required in RapidIO, the identity of the device is independent of its geographic location, but the identifier can be assigned in other ways.
1.2.2.3 Performance characteristics
The header is as small as possible to reduce the control cost, making the package more efficient in organization, packaging and disassembly.
Broadcast and multicast can be achieved by interpreting information in an interconnected structure.
1.2.3 Physical layer characteristics1.2.3.1 Functional characteristics
RapidIO provides flow control between communicating devices because it is impossible for any device to achieve unlimited data buffering.
1.2.3.2 Physical characteristics
The connection can be: point-to-point one-way, one-in-one-out, 8-bit or 16-bit port
The physical layer protocol and packet format are somewhat independent of the physical interconnect topology, however, the physical structure assumption is chained
Does not depend on the bandwidth or delay of the physical structure
Physical layer protocol handles out-of-order and ordered packet transmission and reception
Physical layer protocol tolerates transient errors in the system due to high frequency operation or excessive noise
1.2.3.3 Performance characteristics
Physical protocol and packet format allow for minimum to maximum data compliance
The Baotou is as small as possible. In order to reduce the control cost, the package is more efficient in organization, packaging and disassembly.
The system allows concurrent transactions to prevent wasting system potential performance
Electrical characteristics allow for the highest possible speed. For the future.

15v wall charger,15 Watt Power Supply,15v ac dc adapter,AC Wall Charger Power Adapter,AC/DC Charger Power Supply Switching Adapter,DC 15V Global AC / DC Adapter,15VDC Power Supply Cord Cable Wall Charger,15VDC800 Charger PSU
Shenzhen Waweis Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.szwaweischarger.com